Token and Cryptocurrency Explained For Beginners

Ever heard the words token and cryptocurrency thrown around like they’re the same thing? You're not alone. It's a common mix-up, but the difference is actually pretty straightforward once you get it.
Think of it this way: a cryptocurrency is the native currency of its own blockchain. It's like how the US Dollar is the official currency of the United States. On the other hand, a token is a digital asset built on top of an existing blockchain—kind of like a concert ticket or a gift card that only has value within the US economy.
Unpacking The Core Concepts
Let's stick with that analogy for a minute to really let it sink in.
Imagine the Ethereum blockchain is a huge, digital country. It has its own economy, its own rules, and its own infrastructure. To get anything done in this country—whether that’s sending money or using an app—you have to pay a small fee. That fee is always paid in the country's official currency, which is Ether (ETH).
In this picture, Ether is the cryptocurrency. It's the lifeblood of the whole system, fundamental and independent.
Now, think about all the businesses that could set up shop inside this digital nation. A concert promoter might sell tickets. A local coffee shop could hand out loyalty points. A startup could issue shares of stock. All of these things are tokens.
A token represents a specific asset or utility, but it needs the host country's (the blockchain's) infrastructure and currency (the cryptocurrency) to work. You'd buy that concert ticket token using Ether, and the transaction to get that ticket into your wallet would also be paid for in Ether.
Why The Distinction Matters
Getting this difference down is your first step to really understanding the Web3 world. Even though they both live on the blockchain, cryptocurrencies and tokens play completely different roles.
Cryptocurrencies are the base layer. They're the "gas" that makes the whole machine run. They’re brought into existence through complex processes like mining or staking, which are vital for keeping the blockchain secure and operational. Bitcoin (BTC) on the Bitcoin network and Ether (ETH) on Ethereum are the classic examples.
Tokens are built for specific jobs. Developers create them on established platforms like Ethereum, Solana, or Base without having to build a new blockchain from scratch. This makes creating them much easier, which is why we see a huge variety of them—from representing ownership of a one-of-a-kind digital painting (an NFT) to giving you voting power in a decentralized project.
So, the key takeaway is this: every cryptocurrency has its own dedicated blockchain, but tokens are more like hitchhikers, using existing blockchains to get around. A token and cryptocurrency are not interchangeable terms. One is the native money for a digital nation, and the other represents all the cool assets that can exist within it. This core concept will help you see how everything fits together in this new digital economy.
Understanding Cryptocurrencies: The Blockchain's Native Money

To really get the difference between a token and a cryptocurrency, we need to start with the basics. Cryptocurrencies aren't just a type of digital cash; they're the lifeblood of their own blockchain. Think of a cryptocurrency as being native to its network—it’s baked right into the blockchain's core code.
Here's a simple analogy: a car's engine. That engine is built to run on a specific fuel, whether it's gas, diesel, or electricity. A blockchain works the same way. The Bitcoin network needs Bitcoin (BTC) to run, and the Ethereum network needs Ether (ETH). Simple as that.
This "fuel" is what pays for everything happening on the network—like transaction fees and running smart contracts. It's also used to reward the people who keep the whole system secure and operational. Without its native coin, a blockchain just wouldn't work.
The Two Big Jobs of a Cryptocurrency
So, beyond just keeping the lights on, what do cryptocurrencies actually do? They mostly fill two roles that should feel pretty familiar because they mimic what we expect from regular money.
A Medium of Exchange: This is the most obvious one. You can use something like Bitcoin to buy a coffee or a new laptop, just like you’d use dollars. It's all about sending value directly from one person to another without a bank getting in the middle.
A Store of Value: This is about holding onto its value over time. People buy and hold cryptocurrencies, much like they would gold, with the hope that its purchasing power will hold steady or even grow. It's a long-term play.
This dual purpose is a big reason for the massive buzz and growth in the space. The global crypto market was valued at around USD 6.78 billion in 2024 and is expected to shoot past USD 15 billion by 2030. It's clear this isn't just a passing trend.
A cryptocurrency is the sovereign currency of a decentralized digital nation. It's not just an asset on the blockchain; it is the economic engine of the blockchain itself, created to secure the network and enable value transfer within it.
So, Where Do Cryptocurrencies Come From?
Unlike tokens, which are usually built by projects on top of an existing blockchain, native cryptocurrencies are created through some pretty intense and complex processes. These methods are designed to be decentralized and super secure.
The two main ways they come into existence are:
Mining (Proof-of-Work): Picture a massive, worldwide race where supercomputers compete to solve a tough math problem. The first one to crack it gets to add the next batch of transactions (a "block") to the chain and earns a reward of brand-new coins. This is how Bitcoin is born.
Staking (Proof-of-Stake): This is a much more energy-friendly approach. Instead of racing, people lock up some of their existing crypto as a "stake" in the network. By doing this, they help validate transactions and keep things secure. As a thank you for their help, they get rewarded with new coins. This is the model Ethereum switched to.
Getting a handle on how these foundational currencies work is key before we jump into the wild world of tokens. If you're ready to get your hands on some, our guide on how to buy decentralized crypto is a great place to start.
A Look at the Diverse World of Crypto Tokens
If cryptocurrencies are the native money of a blockchain, then tokens are everything else you can build on top of it.
It helps to think of a blockchain like Ethereum as an operating system—let's say, like iOS on your iPhone. While Apple provides the core iOS platform, developers are the ones who build millions of unique apps that actually run on it. Tokens are just like those apps.
They're built on existing blockchains but are designed for a huge range of specific jobs. This is what makes the dynamic between a token and cryptocurrency so powerful. The crypto (like ETH) keeps the network secure and running, while tokens bring all sorts of utility and new ideas to the party. Let's break down the main types you'll run into.
This infographic gives a simple visual breakdown of the most common token types and how they all fit together.
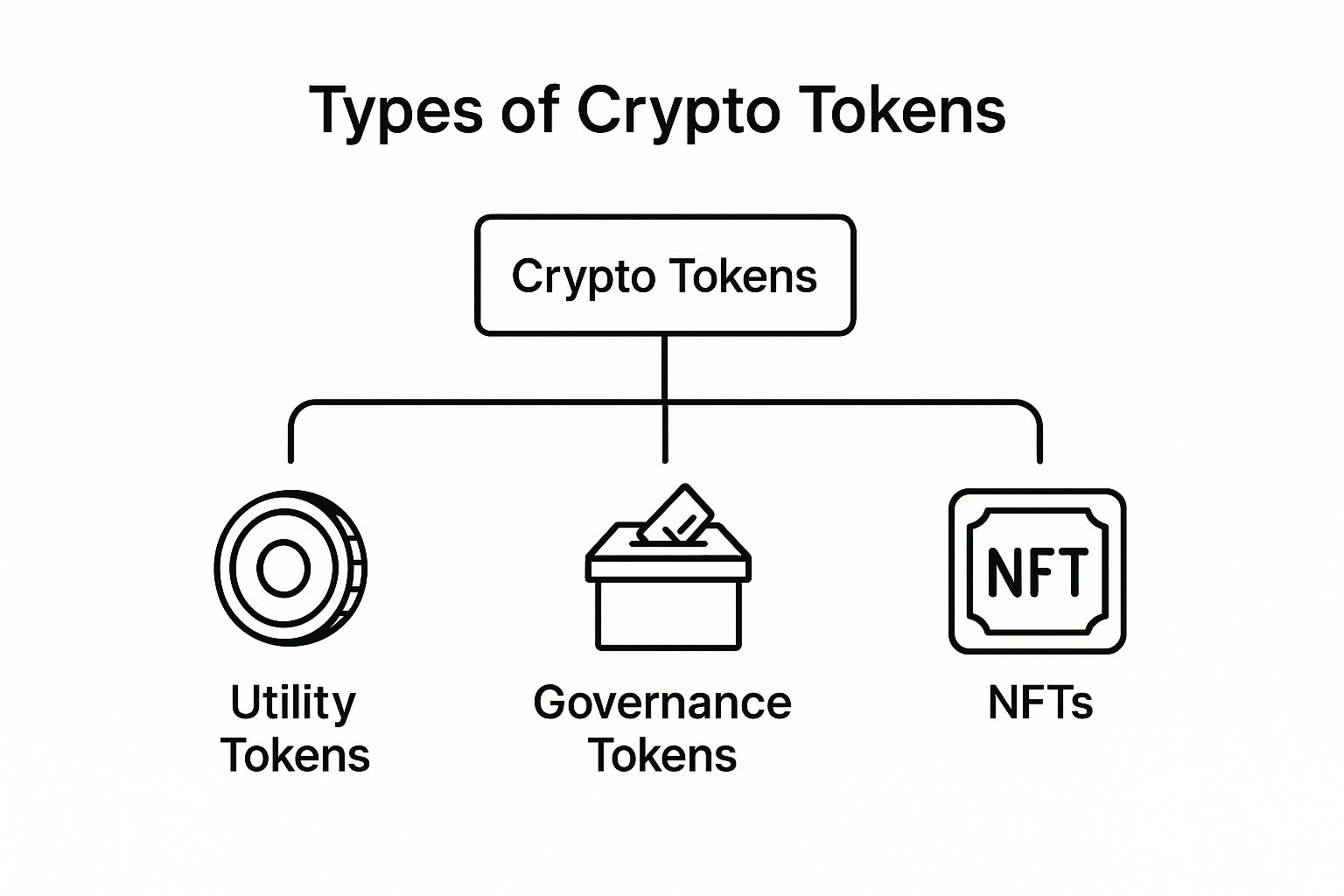
As you can see, the broad world of crypto tokens quickly branches out into specialized categories, each with its own unique role in the ecosystem.
Cryptocurrency vs Token At A Glance
Before we get into the different token types, this table gives you a quick side-by-side comparison to help lock in the core differences.
| Attribute | Cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin, Ether) | Token (e.g., UNI, LINK, SHIB) |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | Operates on its own native blockchain. | Built on top of an existing blockchain (e.g., Ethereum). |
| Purpose | Primarily used as a store of value or medium of exchange to power the network. | Represents an asset or utility for a specific project or dApp. |
| Creation | Created through a complex process like mining or staking. | Can be created relatively easily using smart contract standards. |
| Analogy | Like the native currency of a country (USD, EUR). | Like an arcade token, concert ticket, or company share. |
This at-a-glance view shows how cryptocurrencies are the foundational layer, while tokens are the application layer where most of the specialized activity happens.
Utility Tokens: The Keys to the Kingdom
Utility tokens are easily the most common type you'll encounter. The best way to think of them is as digital arcade tokens or access passes. They don't give you ownership in a company; instead, they give you the right to use a product or service.
A fantastic real-world example is the Basic Attention Token (BAT). If you use the Brave browser, you can opt-in to earn BAT for viewing privacy-friendly ads. You can then turn around and use those tokens to tip your favorite content creators, creating a whole new economy built around attention.
Here are a few common jobs for utility tokens:
- Accessing a Service: Some platforms require you to hold or spend their native token to unlock certain features.
- Paying Internal Fees: Within a specific app, its utility token might be the only accepted currency for transactions.
- Earning Rewards: You can often earn utility tokens by engaging with a platform, like playing a game or contributing data.
Governance Tokens: A Voice in the Project
Next up are governance tokens. These are cool because they give holders actual voting rights in a decentralized project. Imagine owning a tiny slice of the decision-making power for a protocol you use every day. That’s exactly what these tokens do.
Holders can vote on proposals that literally shape the future of the project. We're talking about things like changing transaction fees, deciding how to spend funds from a community treasury, or green-lighting new features. For example, holders of the UNI token can vote on proposals that impact the Uniswap decentralized exchange.
Governance tokens are a cornerstone of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). They transform passive users into active stakeholders, creating a community-driven model where the people who use a project also get to help steer its direction.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Proving Unique Ownership
And finally, we have Non-Fungible Tokens, or NFTs. Unlike a dollar bill or a Bitcoin—which are interchangeable (fungible)—each NFT is completely unique and can't be replaced one-for-one with another.
This special quality of uniqueness makes them the perfect tool for representing ownership of one-of-a-kind items, both digital and physical. This could be anything from a piece of digital art or an in-game collectible to a concert ticket or even the deed to a house. The blockchain acts as a public, unbreakable record proving who owns that specific asset.
If you want to go a bit deeper, our detailed guide explains more about what are tokens in cryptocurrency and shows off even more of their applications.
How Digital Assets Are Created And Distributed
So, where do all these digital assets actually come from? The way a cryptocurrency and a token are brought into the world couldn't be more different, and it really highlights their distinct roles in the whole Web3 space.
For cryptocurrencies, the creation process is woven directly into the fabric of the blockchain's security and operation. It's an intense, fundamental part of the system. Tokens, on the other hand, are typically whipped up by a specific project team to get funding, build a community, or power their app.
How Cryptocurrencies Are Born
Native cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, are created through complex, decentralized processes that are essential for keeping the network secure and running. You can think of it as the digital equivalent of a central bank minting a nation's currency.
The two main ways this happens are:
Mining (Proof-of-Work): Picture a massive, worldwide race where powerful computers are all trying to solve a ridiculously hard math problem. The first one to crack it gets to add the next "block" of transactions to the chain and, as a reward, receives brand-new coins. This is the famous, energy-hungry process that powers Bitcoin.
Staking (Proof-of-Stake): This is the newer, more energy-friendly kid on the block. Instead of a computational race, users lock up some of their existing crypto as collateral to help validate transactions and secure the network. It's kind of like putting your money in a savings bond; by helping maintain the system, you earn rewards paid out in new coins.
How Tokens Enter The World
Making and handing out tokens is usually a much simpler affair, mainly because they don't have the heavy burden of securing an entire blockchain. They're just hitching a ride on an existing one. Their launch is all about one thing: getting a new project off the ground.
For tokens, the launch is a strategic event. It’s about raising funds, getting the token into the hands of early believers, and building a community from day one. It’s less about network security and all about project economics.
Here are the most common ways tokens get out there:
Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs): This is basically crowdfunding, but for crypto. A project team creates a bunch of tokens and sells them to early investors to raise the cash needed for development.
Airdrops: Think of these as a promotional giveaway. A project drops free tokens directly into the crypto wallets of a specific audience—maybe early users of their app or members of a similar community. It's a fantastic tactic for creating buzz and rewarding loyalty right from the start.
These launches are often part of a bigger plan called a Token Generation Event (TGE). If you want to dive deeper into how new digital assets are launched, check out our guide on the TGE meaning in crypto. Each of these methods really shapes the first chapter of a new token or cryptocurrency's life.
How Tokens Are Changing Business And Marketing

When you look past all the speculation, the real power of tokens and cryptocurrency is how they’re becoming serious tools for business. Tokens are giving brands a completely new way to build loyalty, grow communities, and connect with customers on a much deeper level.
Think about the old-school, points-based loyalty programs. They’re fine, but they often feel a little hollow. Web3 is flipping that script by turning customers from passive buyers into genuinely invested members of a community.
Picture a local coffee shop. Instead of earning abstract points, what if you earned their unique utility tokens? You could use those tokens to get early access to a new single-origin roast, snag a free croissant, or even vote on the next seasonal latte. Suddenly, you have something with tangible value and a real sense of participation that a simple punch card can’t replicate.
Creating A Shared Sense Of Ownership
One of the coolest things tokens do for businesses is create a genuine feeling of shared ownership. When customers hold a brand's tokens, they aren’t just customers anymore—they’re part of the ecosystem. This shift is a massive deal for building the kind of loyalty that sticks.
An NFT, for instance, can be much more than a digital collectible. It can be a lifetime pass to a brand’s exclusive events or the key that unlocks a private members-only Discord. This isn't a gimmick; it’s a tradable asset that gives the holder a real, verifiable stake in the community. The entire dynamic changes from a one-way transaction to a two-way partnership.
By distributing tokens, brands are effectively giving their biggest fans a piece of the action. This cultivates a powerful community of advocates who are financially and emotionally invested in seeing the brand succeed.
This evolution is happening as the market itself matures. We're seeing AI and crypto merge, with AI-related tokens now valued at over $39 billion. On top of that, $485 million in recent venture capital has poured into blockchain startups, signaling huge confidence in their real-world business potential. You can dive deeper into these cryptocurrency market trends to see just how fast things are moving.
Real-World Token Marketing Strategies
So, what does this actually look like on the ground? Brands are getting seriously creative with using tokens to pull people through their marketing funnels and get real results.
Here are a few strategies that are already working:
- Token-Gated Content: Brands can lock down exclusive articles, videos, or early product drops so only people holding a specific token or NFT can get in. It’s an instant reward for your biggest supporters.
- NFT-Based Memberships: Projects like Bored Ape Yacht Club basically wrote the playbook on this, using NFTs as membership cards to an exclusive club with both digital and real-world perks.
- Rewarding Engagement: Companies can airdrop utility tokens to users for doing things they already want them to do—like sharing a post, voting in a poll, or trying out a new feature.
These aren’t just clever marketing ploys. Token-based strategies are building the foundation for a new kind of community-first business model, where value flows freely between the brand and its audience.
What's Happening Around the World? A Look at Global Adoption
The story of crypto isn't happening in a vacuum. It's a global phenomenon, and what's fascinating is how different parts of the world are putting their own spin on it. People are adopting this tech not just for kicks, but to solve real, on-the-ground problems specific to their economies.
Take emerging markets, for instance. For millions of people, crypto isn't about speculation; it's a lifeline. It’s a way to send money across borders quickly and cheaply, bypassing slow and expensive traditional systems. This is about financial inclusion, plain and simple—giving people a chance to plug into the global economy like never before.
Different Places, Different Priorities
Now, shift your gaze to more developed countries, and you'll see a completely different picture. Here, the excitement is often around building out the complex world of decentralized finance (DeFi) or exploring what digital ownership really means with NFTs. This is where the tech is being pushed to its limits, creating new ways to invest, collect art, and build online communities.
It's clear that digital assets have grown up. They're no longer just something to invest in; they're becoming foundational tools woven into the fabric of the global economy, used for everything from daily payments to highly sophisticated financial instruments.
And the numbers back this up. Europe is a massive player in the space. Over in the Asia-Pacific region, things have absolutely exploded, with total crypto transaction volume jumping from $1.4 trillion to a staggering $2.36 trillion. A huge part of that growth comes from powerhouses like India.
This incredible surge shows just how much blockchain tech is maturing, making everything from transactions to complex DeFi platforms faster and more accessible. To get a deeper dive, check out this great breakdown of the regional cryptocurrency market and its trajectory.
Frequently Asked Questions
It's totally normal to have a bunch of questions when you're diving into the world of tokens and crypto. Let's break down some of the most common ones to help clear the air.
Is A Stablecoin A Token Or A Cryptocurrency?
This is a great question because stablecoins, like USDC or Tether (USDT), are a bit of a hybrid.
Technically speaking, most stablecoins are tokens. They don't have their own blockchain. Instead, they're built to run on top of existing networks like Ethereum.
But here's the twist: they're designed to behave like a currency. Their whole purpose is to maintain a steady value, usually pegged 1:1 to a fiat currency like the U.S. dollar. This makes them a dependable way to transact, giving you the stability of old-school money with the speed of crypto.
Can A Token Ever Become A Cryptocurrency?
Absolutely, but it's a massive leap. A project often starts by launching its asset as a token on a well-known blockchain, like Ethereum. This is a smart way to get up and running without having to build everything from scratch.
Down the road, if the project really takes off, the team might decide it's time to build their own independent blockchain. Once they launch this new "mainnet," they can move their original tokens over, and just like that, those tokens become the native cryptocurrency of the new network. It’s a complex process, but it signals that a project has truly come into its own.
A good analogy is a startup that initially rents a few desks in a coworking space (the existing blockchain). If they grow big enough, they might decide to build their own custom headquarters (a new, native blockchain). Their "company points" then become the official currency for everything happening in that new building.
Do I Need Cryptocurrency To Buy A Token?
Most of the time, yes. Because tokens live on a host blockchain, you need that blockchain's native cryptocurrency to cover the transaction fees, which you'll often hear called "gas."
For instance, if you want to buy a token built on Ethereum, you’ll need some Ether (ETH) in your wallet. That ETH is what you use to pay the network validators to process your transaction and get that new token into your hands. Think of it as the fuel needed to power any and all activity on the network.
Ready to turn your community members into active participants? With Domino, you can launch engaging, reward-based campaigns in minutes, no code required. Drive real growth and build lasting loyalty. Find out more at https://domino.run.
Level Up Your dApps
Start using Domino in minutes. Use automations created by the others or build your own.
